In the realm of project management, one of the most critical factors that can determine the success or failure of a project is how well stakeholders are managed. Stakeholder analysis is a powerful tool that helps project managers and teams identify, understand, and manage the expectations and influences of all parties involved in a project. This blog post will delve into what stakeholder analysis is, why it’s important, the steps involved in conducting a stakeholder analysis, and best practices to ensure effective stakeholder management.
What is Stakeholder Analysis?
Stakeholder analysis is the process of identifying individuals or groups that are affected by or can affect a project, understanding their needs and expectations, and assessing their level of influence and interest. Stakeholders can be internal, such as team members and executives, or external, such as customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies.
Why is Stakeholder Analysis Important?
- Enhanced Communication: Understanding who your stakeholders are and what they expect allows for more effective and targeted communication. This ensures that stakeholders are kept informed and engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
- Risk Management: By identifying and analyzing stakeholders early, potential risks related to their expectations or influence can be anticipated and mitigated. This proactive approach helps in avoiding conflicts and delays.
- Increased Support and Buy-In: Engaging stakeholders and addressing their concerns increases their support and buy-in for the project. This is crucial for securing necessary resources and ensuring smooth project execution.
- Alignment of Objectives: Stakeholder analysis helps in aligning the project objectives with the expectations of key stakeholders, ensuring that the project delivers value and meets its goals.
Steps in Conducting Stakeholder Analysis
- Identify Stakeholders: List all potential stakeholders, both internal and external, who are involved in or affected by the project. This includes team members, managers, customers, suppliers, regulatory agencies, and the community.
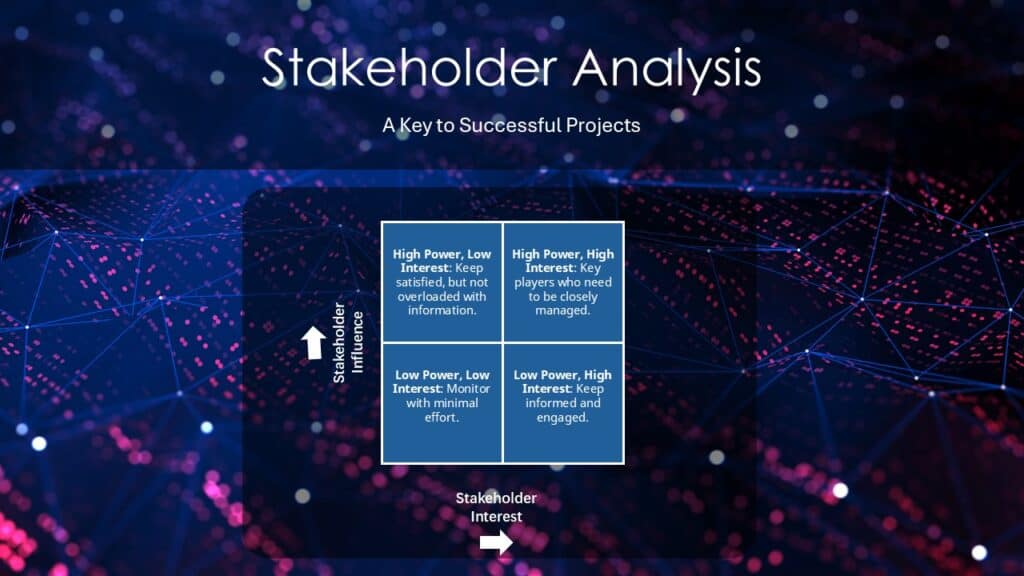
- Classify Stakeholders: Categorize stakeholders based on their level of influence and interest. A common tool used for this purpose is the Power/Interest Grid:
- High Power, High Interest: Key players who need to be closely managed.
- High Power, Low Interest: Keep satisfied, but not overloaded with information.
- Low Power, High Interest: Keep informed and engaged.
- Low Power, Low Interest: Monitor with minimal effort.
- Understand Stakeholder Needs and Expectations: Conduct interviews, surveys, or meetings to gather detailed information about stakeholders’ needs, expectations, and any potential concerns or issues they may have regarding the project.
- Assess Stakeholder Influence and Impact: Evaluate the level of influence each stakeholder has on the project and how the project impacts them. This helps in prioritizing stakeholders and determining the level of engagement required.
- Develop Stakeholder Management Strategies: Based on the analysis, develop tailored strategies for managing each stakeholder or group of stakeholders. This includes defining communication plans, engagement activities, and methods for addressing their concerns and expectations.
- Implement and Monitor: Execute the stakeholder management plan, ensuring continuous communication and engagement. Regularly monitor and reassess stakeholder relationships and adjust the strategies as necessary.
Best Practices for Effective Stakeholder Management
- Engage Early and Often: Start engaging stakeholders early in the project and maintain regular communication throughout. This helps in building trust and ensures stakeholders feel valued and heard.
- Be Transparent: Share information openly and honestly with stakeholders. Transparency builds trust and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Tailor Communication: Customize communication based on the stakeholder’s preferences, influence, and interest. Use appropriate channels and levels of detail to ensure messages are effectively received and understood.
- Be Proactive: Anticipate potential issues and address them before they escalate. Proactive management helps in maintaining positive relationships and preventing conflicts.
- Seek Feedback: Regularly seek feedback from stakeholders to understand their satisfaction levels and areas for improvement. This feedback loop helps in continuously improving stakeholder management practices.
- Document and Track: Maintain detailed records of stakeholder interactions, agreements, and changes in their influence or interest. This documentation helps in tracking progress and ensuring accountability.
Stakeholder Analysis in Agile Projects
In Agile projects, stakeholder analysis and management are dynamic and continuous processes. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, emphasize collaboration, flexibility, and iterative progress, which align well with effective stakeholder management.
Key Practices in Agile Stakeholder Management:
- Product Owner Role:
- The Product Owner (PO) acts as the primary liaison between the development team and the stakeholders. The PO is responsible for understanding stakeholder needs, prioritizing them, and ensuring the team delivers value.
- The PO maintains the Product Backlog, which includes user stories and features prioritized based on stakeholder input.
- Continuous Engagement:
- Agile projects involve stakeholders continuously rather than at predefined stages. This is facilitated through regular interactions such as sprint reviews, where stakeholders can see the product increment and provide feedback.
- Regular communication ensures that stakeholder needs are understood and met, and any changes or new requirements are quickly integrated.
- Feedback Loops:
- Agile practices emphasize short development cycles (sprints) with frequent feedback loops. This allows the team to adapt to stakeholder feedback and changing requirements swiftly.
- Tools like user story mapping and backlog refinement sessions help in aligning the team’s work with stakeholder expectations.
- Transparency and Visibility:
- Agile frameworks promote transparency and visibility of the project’s progress. Tools like burn-down charts, sprint backlogs, and information radiators provide stakeholders with real-time updates on the project’s status.
- Daily stand-ups (Scrum meetings) and sprint reviews keep stakeholders informed and engaged, fostering a collaborative environment.
- Prioritization and Value Delivery:
- Stakeholder analysis helps in identifying and prioritizing features and user stories that deliver the most value. Techniques like MoSCoW (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won’t have) and Value vs. Effort matrices aid in this process.
- The Agile focus on delivering small, incremental releases ensures that stakeholders see continuous value and can provide timely feedback.
Steps for Effective Stakeholder Management in Agile:
- Identify and Categorize Stakeholders: Identify all stakeholders and classify them based on their influence and interest using tools like the Power/Interest Grid.
- Engage and Collaborate: Regularly engage stakeholders through meetings, demos, and collaborative sessions. Use tools like user story workshops and sprint reviews to gather feedback and ensure alignment.
- Prioritize and Adapt: Continuously prioritize stakeholder needs and adapt to changes. Maintain a flexible and dynamic Product Backlog that reflects the evolving requirements.
- Communicate Transparently: Ensure open and honest communication. Use visual tools and regular updates to keep stakeholders informed about progress, challenges, and changes.
- Iterate and Improve: Use iterative cycles to gather feedback and improve continuously. Involve stakeholders in retrospectives to understand their perspective and make necessary adjustments.
Conclusion
Stakeholder analysis is an essential component of successful project management. By systematically identifying, understanding, and managing stakeholders, project managers can ensure that projects are delivered on time, within scope, and with the full support of all involved parties. Effective stakeholder management not only mitigates risks but also enhances communication, fosters collaboration, and ultimately leads to the successful realization of project goals. By following the steps and best practices outlined in this blog post, you can master the art of stakeholder analysis and drive your projects to success. In Agile projects, this approach is even more dynamic and integrated, ensuring that stakeholder needs are continuously met and that the project remains aligned with its goals and objectives.